Ear Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Best Treatment Methods
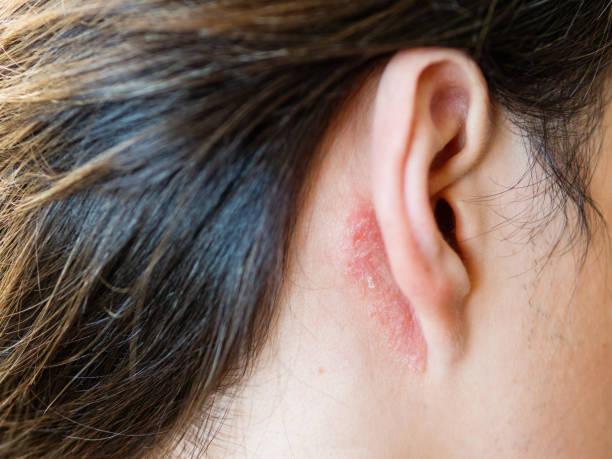
Ear Eczema is a form of eczema that affects the delicate skin of and around the ears. It can be incredibly frustrating and uncomfortable, often leading to itching, redness, flaking, and even pain. While eczema is a chronic condition that can affect many areas of the body, the ears are especially sensitive due to their thin skin and frequent exposure to allergens, irritants, and environmental changes.
In this blog, we'll explore everything you need to know about ear eczema—including what causes it, how it presents, how it's diagnosed, and most importantly, the best treatment methods available to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
What is Ear Eczema?
Ear eczema is a localized form of eczema that can affect:
-
The outer ear (pinna)
-
The ear canal (leading to otitis externa)
-
The area behind the ears
-
The earlobes
Like other types of eczema, it involves inflammation of the skin, which can lead to itching, redness, dryness, and flaking. In some cases, it may cause small blisters or weeping sores if the area becomes infected or severely irritated.
While anyone can develop ear eczema, it is most commonly seen in people with a history of atopic dermatitis, allergies, or sensitive skin.
Types of Ear Eczema
There are several types of eczema that may affect the ears:
1. Atopic Dermatitis
This is a chronic inflammatory condition that usually begins in childhood. It’s commonly associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever. In people with atopic dermatitis, ear eczema often coexists with eczema on the face, neck, or scalp.
2. Contact Dermatitis
This occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an allergen or irritant. Common triggers include:
-
Nickel (in earrings)
-
Hair dyes
-
Shampoo or conditioner
-
Hearing aids or earbuds
-
Detergents and soaps
3. Seborrheic Dermatitis
This type affects oily areas of the skin and may be linked to an overgrowth of yeast. It often causes red, flaky patches in and around the ears and scalp.
4. Asteatotic Eczema (Eczema Craquelé)
Usually seen in older adults, this form occurs when the skin becomes overly dry, leading to cracked and itchy skin. The ears can be affected, especially during colder months.
Causes and Triggers of Ear Eczema
The underlying cause of eczema is not entirely understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Here's a look at some common factors that may contribute to ear eczema:
1. Allergens and Irritants
-
Nickel in earrings
-
Fragranced hair or skin products
-
Hearing aids made from irritating plastics
-
Sweat and heat
2. Weather Conditions
-
Cold, dry air can exacerbate eczema by stripping moisture from the skin.
-
Hot and humid environments may increase sweating and irritation.
3. Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly in women, can worsen eczema symptoms.
4. Stress
While not a direct cause, stress can weaken the immune system and lead to flare-ups.
5. Infections
A secondary infection, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, can worsen symptoms and require antibiotic treatment.
Common Symptoms of Ear Eczema
Ear eczema can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically include:
-
Itching (often intense and persistent)
-
Redness or inflammation
-
Dryness and scaling
-
Cracks or fissures in the skin
-
Weeping or oozing if the skin is broken
-
Crusting or scabbing
-
Soreness or burning sensation
-
Hearing issues if eczema affects the ear canal and causes blockage
In cases where eczema affects the inner ear, it may cause a sensation of fullness or mild hearing loss due to swelling and flaking blocking the ear canal.
Diagnosing Ear Eczema
A healthcare provider, typically a dermatologist or ENT specialist, can diagnose ear eczema through a physical examination and a detailed medical history. If necessary, additional tests may be performed:
-
Patch testing to identify allergens (especially for contact dermatitis)
-
Swabs or cultures to check for bacterial or fungal infections
-
Dermatoscopy to examine the skin surface more closely
Prompt diagnosis is essential to prevent complications, such as ear infections or chronic otitis externa (swimmer’s ear).
Best Treatment Methods for Ear Eczema
While there’s no permanent cure for eczema, a combination of lifestyle adjustments, skincare, and medical treatments can keep flare-ups under control and provide significant relief.
1. Skincare and Self-Care
Proper daily care is the foundation of eczema management. Here's what you can do:
-
Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers
Avoid soaps with alcohol, sulfates, or artificial fragrances.
-
Moisturize daily
Apply emollients like petroleum jelly or fragrance-free creams to keep the skin hydrated.
-
Avoid scratching
Scratching can worsen inflammation and lead to infection.
-
Protect ears from the elements
In cold weather, wear ear covers. During summer, protect from excessive sun and sweat.
-
Be cautious with earphones or hearing aids
Clean regularly and ensure they're made from non-irritating materials.
2. Topical Treatments
-
Topical corticosteroids
Mild steroids like hydrocortisone can reduce inflammation and itching. Use under medical supervision, especially near the ear canal or inner ear.
-
Calcineurin inhibitors
Non-steroidal creams like tacrolimus (Protopic) or pimecrolimus (Elidel) are effective for sensitive areas such as the face and ears.
-
Antifungal creams
If seborrheic dermatitis is suspected, antifungal agents like ketoconazole may be prescribed.
3. Medications
-
Oral antihistamines
These help reduce itching and may be especially useful at night.
-
Antibiotics or antifungals
If an infection is present, your doctor may prescribe topical or oral medications.
-
Systemic immunosuppressants
For severe or chronic eczema, drugs like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be considered.
-
Biologic therapies
New medications like dupilumab (Dupixent) are targeted treatments for atopic dermatitis and have shown promise for difficult cases.
4. Ear Canal Involvement
If eczema affects the inside of the ear, treatment becomes more delicate. A healthcare professional may:
-
Prescribe steroid ear drops
-
Use ear wicks to deliver medication deep into the canal
-
Advise ear cleaning by a professional to avoid damage or infection
Self-treating internal ear eczema without guidance can lead to serious complications, including hearing damage or chronic infections.
Preventing Flare-Ups
Prevention is just as important as treatment when it comes to managing ear eczema. Here are some practical strategies:
-
Keep your ears clean and dry.
-
Avoid using cotton swabs inside the ear canal.
-
Limit use of earrings that contain nickel or other allergenic metals.
-
Perform a patch test before using new skin or hair products.
-
Maintain a healthy, anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s and antioxidants.
-
Manage stress through yoga, meditation, or therapy.
When to See a Doctor
Seek professional care if:
-
Symptoms do not improve with over-the-counter treatment
-
The skin is oozing or crusted over
-
Pain or hearing loss occurs
-
You suspect an allergic reaction or infection
-
Eczema spreads to other parts of your body
A dermatologist or ENT specialist can tailor a treatment plan that addresses your specific type and severity of eczema.
Living with Ear Eczema
While ear eczema can be persistent, most people can successfully manage the condition with proper care. It may take time to identify your unique triggers and find the right combination of treatments, but don’t lose hope.
Keeping a symptom diary, practicing consistent skincare, and staying informed about your condition will greatly improve your quality of life. If your eczema is particularly stubborn or severe, speak to your doctor about emerging therapies or new options available through Clinical Trials of Atopic Dermatitis.
- Information Technology
- Office Equipment and Supplies
- Cars and Trucks
- Persons
- Books and Authors
- Tutorials
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



