Can China really encircle India with its String of Pearls? The great game of Asia
Chinese naval vessel is in the Pakistani waters in the Arabian Sea off Karachi. The naval forces of China and Pakistan are holding joint exercises raising concerns for geostrategic assets of India.
Many observers have pointed out that Chinese activities in the Arabian Sea off Pakistan coast have increased significantly. China has called this a move to pirates in the region.
China was given the authority to manage Gwadar port of Pakistan near Iran border for next 40 years. The port was developed by China. Also, there is China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). China is concerned about the security of the CPEC but it is also using the project to deepen its strategic assets in the northern Indian Ocean.
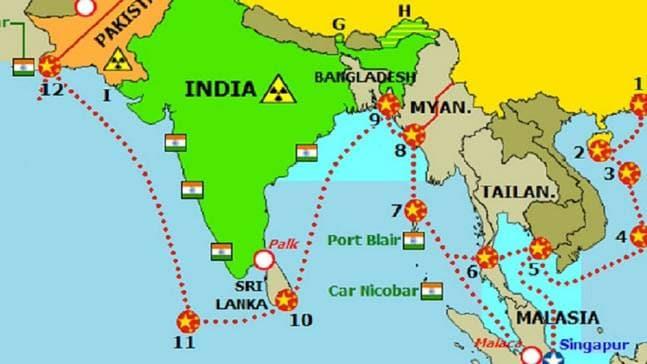
STRING OF PEARLS
Those having slightest of interest in India-China relationship are familiar with the String of Pearls theory. The phrase seems to have been in use even before but publication of Energy Futures in Asia: Final Report in 2004 made it popular.
The report said that China was working on a strategy to expand its influence in the Indian Ocean to extract maximum benefit from it and contain Indian hold in the region. China was expected to raise civilian and military infrastructure at chosen points on the islands or ports - metaphorically called pearls - surrounding India.
String of pearl, in geostrategic parlance, refers to the Strait of Malacca, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, the Maldives, the Strait of Hormuz and Somalia. It also includes Bangladesh and Myanmar in Chinese strategy.
STRAIT OF MALACCA
The Strait of Malacca connects Indian Ocean with Pacific Ocean with Malaysia and Singapore on one side while Indonesia on the other side. It is not very far from the Nicobar Islands.
The Strait of Malacca is key for China's energy requirements. About 80 per cent of its fuel from the Middle East passes through this. Wary of India's stronghold in the Indian Ocean, China has been consistently working to develop friendly and cooperative relations with the countries in the region.
In 1971, when China gave feelers about aligning with Pakistan during the Liberation War for Bangladesh, India had threatened to block the Strait of Malacca. Later in 1999 during Kargil war, India choked supply to Pakistan - practically blocking Karachi port - using its dominance in the Indian Ocean. China is on a mission to turn the tide against India.
MYANMAR AND BANGLADESH
China has developed assets in Myanmar. It has built a gas pipeline of about 2,400 km from Myanmar to China. It is also reported to have a military base in Coco Island of Myanmar.
China is said to have developed a naval base near Strait of Malacca on Cocos Keeling Island, which is a distant part of Australia.
Further north in the Bay of Bengal, China developed the port of Chittagong in Bangladesh. It has given China a foothold and stake in the Bay of Bengal. Significant part of Chinese trade passes through this port.
China had been pushing Bangladesh to allow it to develop a small naval base near Chittagong.
SRI LANKA
Sri Lanka has been a trusted friend of India for decades but the years between 2012 and 2014 saw increased Chinese presence in the island country.
China developed a port at Hambantola on the southeastern part of Sri Lanka. A Chinese company built the port and gained control to manage it.
China was in the process of developing it into a naval base, when in January 2015, the Rajapakshe government was voted out in Sri Lanka. The Sirisena government has had better equation with the Indian government and Chinese plans seem to have received a jolt.
PAKISTAN
China has Gwadar port and the CPEC to protect in Pakistan. The Gwadar port has gained further significance as China joined what was originally conceived as the Iran-Pakistan-India gas pipeline.
India withdrew from the project as it was not assured of the security of the pipeline in certain stretches in Pakistan. The project is now called Iran-Pakistan-China pipeline. It touches Gwadar on its route to China.
The CPEC is developing into a vital geo-strategic and trade asset of China. At present, it carries only two per cent of its trade with Pakistan. But, China expects the volume to increase as it plans to route much of its trade with the Middle East and Africa through Gwadar port and the CPEC.
These two also gives China an alibi to strengthen its military prowess, with active collaboration of Pakistan, in the Indian Ocean particularly around the Strait of Harmuz, which is equally vital for India's international trade.
HOW INDIA COUNTERS CHINA
India has identified the challenge from China's String of Pearls strategy. India has made serious attempts to improve its relation with its maritime neighbours.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recast India's Look East Policy as Act East Policy with emphasis on developing infrastructure in the East Asian countries. To counter Chinese influence in Myanmar, India has recently extended over USD 1.75 billion in grants and credit to Myanmar.
https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/china-encircle-india-string-of-pearls-982930-2017-06-15
- Information Technology
- Office Equipment and Supplies
- Cars and Trucks
- Persons
- Books and Authors
- Tutorials
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



