IAM Technologies and Services Report 2025–2030: Building Trust in the Digital Enterprise
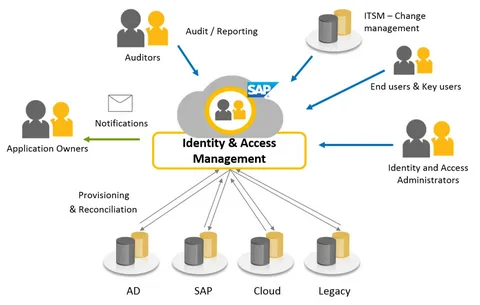
In an era where digital transformation is both a strategic necessity and a cybersecurity challenge, Identity and Access Management (IAM) stands as a foundational pillar in securing digital ecosystems. IAM systems govern how digital identities are created, maintained, and revoked, ensuring that only the right individuals access the right resources at the right times. From cloud-native infrastructure to hybrid enterprises, IAM is essential in preventing data breaches, enabling compliance, and enhancing user experience.
This comprehensive report examines the evolving landscape of the IAM market from 2025 through 2030, spotlighting technological innovations, industry applications, integration strategies, zero trust adoption, and the future of decentralized identity management.
Click here to download the sample report
1. IAM Market Overview: Shifting Paradigms in Identity Security
The traditional concept of identity management—centered on internal networks and perimeter-based defense—has evolved dramatically. With the rise of cloud computing, remote work, mobile access, and IoT devices, identity has become the new security perimeter.
IAM solutions today encompass a range of capabilities, including:
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- User Provisioning and Lifecycle Management
- Role-Based and Attribute-Based Access Control (RBAC & ABAC)
- Identity Governance and Administration (IGA)
These capabilities have become increasingly integrated with Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) models, AI-driven anomaly detection, and user behavior analytics to mitigate insider threats and credential abuse.
2. Key Technology Innovations in IAM
a. Passwordless Authentication
The future of IAM is moving towards passwordless authentication, which leverages biometrics, device-based authentication, and cryptographic keys. This approach not only reduces attack surfaces but also improves user convenience.
b. Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized identity frameworks, built on blockchain or distributed ledger technology (DLT), allow users to own and control their identity data without reliance on centralized authorities. These solutions improve privacy, reduce identity fraud, and enhance user trust.
c. AI and Machine Learning
AI-powered IAM tools can detect anomalies in access patterns, flag suspicious behavior, and automatically adjust access controls. Machine learning enhances the ability to classify user behavior and optimize access permissions dynamically.
d. Cloud-Native IAM
With increasing cloud adoption, IAM solutions are being rearchitected to be cloud-native, supporting multi-cloud and hybrid deployments. This provides flexibility, scalability, and faster integration with other SaaS applications.
e. Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
IDaaS offerings provide IAM capabilities through cloud services, reducing infrastructure complexity and enabling seamless integration across environments. Features include SSO, MFA, directory services, and identity governance on a subscription model.
3. IAM in Action: Industry-Specific Use Cases
a. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, IAM ensures HIPAA-compliant access to electronic health records (EHRs), protecting sensitive patient data. Role-based access allows clinicians, administrative staff, and third-party providers to access only what they need.
b. Manufacturing
Modern manufacturers adopt IAM to secure IoT-connected equipment, manage vendor access, and control internal systems. Identity federation across plant systems ensures seamless and secure access for operational staff.
c. Education
Educational institutions use IAM to authenticate students, staff, and faculty across learning management systems (LMS), campus networks, and cloud services. IAM helps manage the lifecycle of academic and administrative identities efficiently.
d. Government and Public Sector
IAM in government ensures secure digital identities for citizens, supports smart city initiatives, and enables secure internal operations. Strong authentication mechanisms help prevent identity fraud and unauthorized access to critical systems.
e. Financial Services
Financial institutions rely on IAM to meet regulatory mandates and protect customer accounts. Capabilities like customer identity verification (KYC), transaction-level access control, and fraud detection are integrated into IAM platforms.
4. Zero Trust and IAM Convergence
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is revolutionizing access control by replacing the “trust but verify” model with “never trust, always verify.” IAM is at the core of this paradigm, as it provides:
- Continuous authentication and risk assessment
- Dynamic access decisions based on context (location, device, behavior)
- Microsegmentation of access rights
- Just-in-time (JIT) access provisioning
IAM tools increasingly integrate with SIEM, SOAR, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms to enforce Zero Trust principles at scale.
5. IAM for Remote and Hybrid Workforces
The hybrid work model introduces new IAM challenges:
- Managing BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)
- Secure VPN-less access to corporate resources
- Monitoring and auditing user activity
IAM platforms now offer context-aware authentication, geofencing, and device posture checks to accommodate dynamic work environments while safeguarding sensitive resources.
6. Role of IAM in Compliance and Governance
IAM is critical in fulfilling compliance requirements such as access certification, audit logging, and least privilege enforcement. Regulatory frameworks that influence IAM architecture include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act)
- PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
IAM solutions help automate compliance workflows by:
- Enabling segregation of duties
- Generating access reports
- Providing real-time access visibility
7. Challenges in IAM Deployment
Despite its importance, IAM implementation is often complex due to:
a. Legacy Infrastructure
Organizations with outdated IT systems struggle to integrate modern IAM tools, leading to fragmented identity environments.
b. Identity Silos
Disparate identity sources across departments or cloud platforms can result in inconsistent access control and increased risk.
c. User Resistance
Frequent authentication prompts or strict access policies may result in poor user experience and pushback from employees.
d. Insider Threats
IAM must also contend with risks from users with legitimate access, such as privileged users or compromised credentials.
Mitigating these challenges requires careful planning, stakeholder involvement, and ongoing policy refinement.
8. IAM Implementation Strategy
Step 1: Identity Inventory
Begin by identifying all users, devices, applications, and data points that require access control.
Step 2: Define Access Policies
Establish policies for user roles, access levels, authentication methods, and data sensitivity.
Step 3: Choose the Right Platform
Select an IAM solution that supports your infrastructure, scalability needs, and compliance mandates.
Step 4: Integration and Automation
Automate provisioning, deprovisioning, and access approvals. Integrate IAM with HR systems, Active Directory, and cloud platforms.
Step 5: Monitor and Audit
Implement continuous monitoring, logging, and periodic access reviews to maintain control and meet compliance requirements.
9. Future Trends and Roadmap (2025–2030)
a. Hyperautomation in Identity Governance
IAM platforms will incorporate RPA (Robotic Process Automation) and AI to automate identity lifecycle management at scale.
b. IAM and Digital Twins
In industrial sectors, digital twins of employees or devices will be linked with identity attributes to simulate access risks and usage patterns.
c. Cross-Border Identity Collaboration
Interoperable digital identity frameworks will allow secure identity validation across borders for travelers, international students, and remote workers.
d. Quantum-Resistant IAM
IAM solutions will begin integrating quantum-safe cryptography to future-proof against the computational power of quantum systems.
e. Unified Identity Fabric
The future IAM landscape will move toward a unified identity fabric—a platform-agnostic layer that seamlessly governs identities across cloud, on-premise, and edge environments.
10. Conclusion: IAM as a Digital Enabler
As cyber threats become more sophisticated and user environments more complex, identity management will remain the frontline of defense. IAM is no longer just a security function—it’s a business enabler, empowering organizations to operate efficiently, securely, and compliantly in a digital-first world.
The path forward involves embracing Zero Trust principles, deploying intelligent and automated IAM platforms, and ensuring user-centric design that balances security with experience. By doing so, organizations can confidently navigate the digital future with identity as the new perimeter.
- Information Technology
- Office Equipment and Supplies
- Cars and Trucks
- Persons
- Books and Authors
- Tutorials
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



